Crumpled bottle
Some reactions are hotter than others
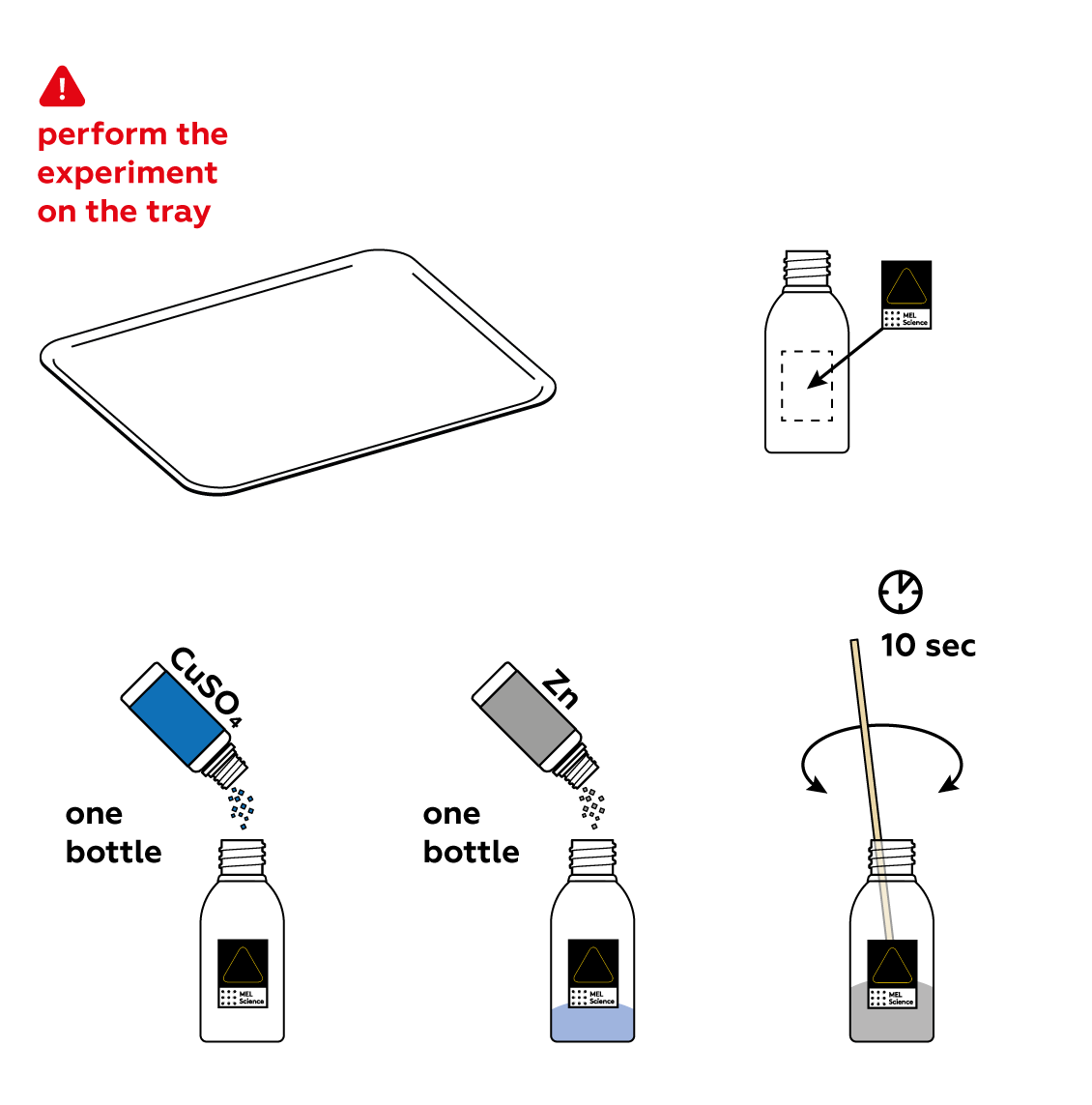
Reagents
Safety
- Put on protective gloves and eyewear.
- Conduct the experiment on the plastic tray.
- Do not allow chemicals to come into contact with the eyes or mouth.
- Keep young children, animals and those not wearing eye protection away from the experimental area.
- Store this experimental set out of reach of children under 12 years of age.
- Clean all equipment after use.
- Make sure that all containers are fully closed and properly stored after use.
- Ensure that all empty containers are disposed of properly.
- Do not use any equipment which has not been supplied with the set or recommended in the instructions for use.
- Do not replace foodstuffs in original container. Dispose of immediately.
- In case of eye contact: Wash out eye with plenty of water, holding eye open if necessary. Seek immediate medical advice.
- If swallowed: Wash out mouth with water, drink some fresh water. Do not induce vomiting. Seek immediate medical advice.
- In case of inhalation: Remove person to fresh air.
- In case of skin contact and burns: Wash affected area with plenty of water for at least 10 minutes.
- In case of doubt, seek medical advice without delay. Take the chemical and its container with you.
- In case of injury always seek medical advice.
- The incorrect use of chemicals can cause injury and damage to health. Only carry out those experiments which are listed in the instructions.
- This experimental set is for use only by children over 12 years.
- Because children’s abilities vary so much, even within age groups, supervising adults should exercise discretion as to which experiments are suitable and safe for them. The instructions should enable supervisors to assess any experiment to establish its suitability for a particular child.
- The supervising adult should discuss the warnings and safety information with the child or children before commencing the experiments. Particular attention should be paid to the safe handling of acids, alkalis and flammable liquids.
- The area surrounding the experiment should be kept clear of any obstructions and away from the storage of food. It should be well lit and ventilated and close to a water supply. A solid table with a heat resistant top should be provided
- Substances in non-reclosable packaging should be used up (completely) during the course of one experiment, i.e. after opening the package.
FAQ and troubleshooting
Wait about 5 minutes. If the reaction does not start, repeat the experiment with a new bottle and reagents, carefully following the steps according to the instructions.
Wait until the beaker has cooled down (the thermochromic sticker should change from yellow to black). Then dispose of the bottle with household waste, and wash the beaker with soap and warm water.
Step-by-step instructions
First, mix some CuSO4 and Zn in a bottle. These substances are keen to react with each other. However, they won't do it just yet. To actually engage in a chemical reaction, they need water.
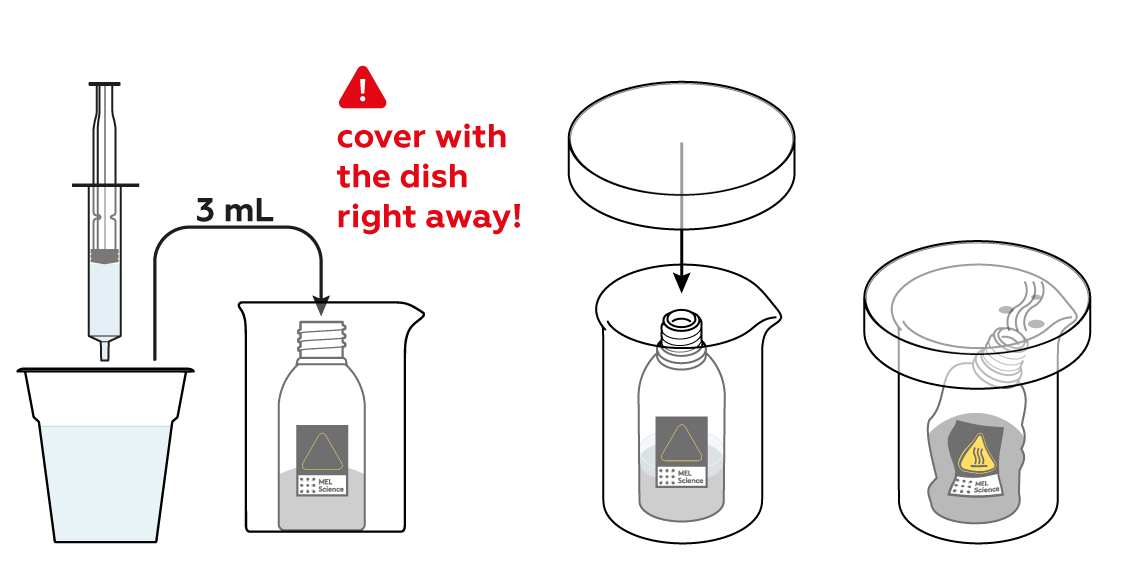
The reaction between CuSO4 and Zn can be quite vigorous, so before getting it started, make sure to place the reagent bottle in the glass beaker.

To initiate the reaction, add some water and watch!
Disposal
- Please refer to local regulations when disposing of chemicals.
- Dispose of other solid waste with household garbage.
Scientific description


and Zn
makes copper Cu
, ZnSO4
, and, well, heat
. Much like small crystals of salt dissolve in water faster than large ones, fine Zn powder reacts with CuSO4 much faster than a large piece of Zn would. As a result, the reaction goes quickly enough to produce a lot of heat in a short amount of time.

Why do some chemical reactions release heat?
Any chemical reaction is the transformation of some substances into others. During this transformation, the atoms themselves stay the same and their number stays constant – they just bind to each other in a different way. This means that old bonds between them are destroyed, and new ones are formed.
Chemical bonds don’t just form or break on a whim. Breaking them takes some “effort” (i.e. energy). And conversely, energy is released when new bonds are formed. It is possible to mathematically calculate how much energy it takes to break old bonds and form new ones. The difference between energy released and energy spent converts into heat during the reaction. If more heat is absorbed than released, the temperature drops, and vice versa: if more heat is released than absorbed, the temperature rises. This change in temperature is called the thermal effect of a reaction.